Extrapolations at highest q¶
superclass of functions for extrapolation of SAS data past available range
- class jldesmear.api.extrapolation.Extrapolation[source]¶
superclass of functions for extrapolation of SAS data past available range
The general case to (forward) slit-smear small-angle scattering involves integration at
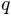 values past any measurable range.
values past any measurable range.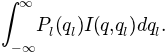
Due to symmetry, the integral is usually folded around zero,thus becoming
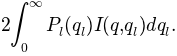
Even when the upper limit is reduced due to finite slit dimension (the so-called slit-length,
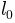 ),
),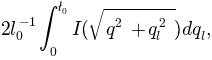
it is still necessary to evaluate
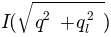 beyond
the last measured data point, just to evaluate the integral.
beyond
the last measured data point, just to evaluate the integral.An extrapolation function is used to describe the
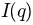 beyond the measured data.
In the most trivial case, zero would be returned. Since this simplification
is known to introduce truncation errors, a model form for the last few
available data points is assumed. Fitting coefficients are determined from
the final data points (in the method fit()) and are used
subsequently to generate the extrapolation at a specific
beyond the measured data.
In the most trivial case, zero would be returned. Since this simplification
is known to introduce truncation errors, a model form for the last few
available data points is assumed. Fitting coefficients are determined from
the final data points (in the method fit()) and are used
subsequently to generate the extrapolation at a specific 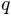 value
(in the method calc()).
value
(in the method calc()).Examples:
See the subclasses for examples implementations of extrapolations.
Example Linear Extrapolation:
Here is an example linear extrapolation class:
import extrapolation class Extrapolation(extrapolation.Extrapolation): name = 'linear' # unique identifier for users def __init__(self): # initialize whatever is needed internally self.coefficients = {'B': 0, 'm': 0} def __str__(self): form = "linear: I(q) = " + str(self.coefficients['B']) form += " + q*(" + str(self.coefficients['m']) + ")" return form def calc(self, q): # evaluate at given q return self.coefficients['B'] + self.coefficients['m'] * q def fit_result(self, reg): # evaluate fitting parameters with regression object (constant, slope) = reg.LinearRegression() self.coefficients = dict(B=constant, m=slope)
Basics:
Create an Extrapolation class which is a subclass of extrapolation.Extrapolation.
The basic methods to override are
- __str__() : string representation
- calc() : determines
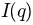 from q and self.coefficients dictionary
from q and self.coefficients dictionary - fit_result() : assigns fit coefficients to self.coefficients dictionary
By default, the base class Extrapolation uses the jldesmear.api.StatsReg module to accumulate data and evaluate fitted parameters. Override any or all of these methods to define your own handling:
See the source code of Extrapolation for an example.
documentation from source code:
- SetCoefficients(coefficients)[source]¶
define the function coefficients
Parameters: coefficients (dict) – named terms used in evaluating the extrapolation
- calc(q)[source]¶
evaluate the extrapolation function at the given q
Note: must override in subclass Parameters: q (float) – magnitude of scattering vector Returns: value of extrapolation function at q Return type: float
- fit(q, I, dI)[source]¶
fit the function coefficients to the data
Note: might override in subclass
Parameters: - q (float) – magnitude of scattering vector
- I (float) – intensity or cross-section
- dI (float) – estimated uncertainty of intensity or cross-section
- fit_add(reg, x, y, z)[source]¶
Add a data point to the statistics registers. Called from fit_loop().
Note: might override in subclass
Parameters: - reg (StatsRegClass object) – statistics registers (created in fit())
- x (float) – independent axis
- y (float) – dependent axis
- z (float) – estimated uncertainty of y
- fit_loop(reg, x, y, z)[source]¶
Add a dataset to the statistics registers for use in curve fitting. Called from fit().
Note: might override in subclass
Parameters: - reg (StatsRegClass object) – statistics registers (created in fit())
- x (numpy.ndarray) – independent axis
- y (numpy.ndarray) – dependent axis
- z (numpy.ndarray) – estimated uncertainties of y
- fit_result(reg)[source]¶
Determine the results of the fit and store them as the set of coefficients in the self.coefficients dictionary. Called from fit().
Example:
def fit_result(self, reg): (constant, slope) = reg.LinearRegression() self.coefficients['B'] = constant self.coefficients['m'] = slope
Note: must override in subclass otherwise fit_result() will raise an exception Parameters: reg (StatsRegClass object) – statistics registers (created in fit())
- fit_setup()[source]¶
Create a set of statistics registers to evaluate the coefficients of the curve fit. Called from fit().
Note: might override in subclass Returns: statistics registers Return type: StatsRegClass object
- jldesmear.api.extrapolation.discover_extrapolations()[source]¶
return a dictionary of the available extrapolations
Extrapolation functions must be in a file named extrap_KEY.py where KEY is the key name of the extrapolation function. The file is placed in the source code tree in the same directory as the module: extrapolation.
The calc() method should be capable of handling q as a numpy.ndarray or as a float.
The file must contain:
- Extrapolation: a subclass of Extrapolation